- 作者:老汪软件技巧
- 发表时间:2024-12-15 17:04
- 浏览量:
引言
在现代Web开发中,如何优雅地保存用户输入并确保其在页面刷新后仍然存在,是一个常见的需求。localStorage 提供了一个简单而强大的解决方案,它允许我们在浏览器中持久化存储数据。本文将通过一个生动的例子——“LOCAL TAPAS”应用,向您展示 localStorage 的魅力。

话不多说,结果展示
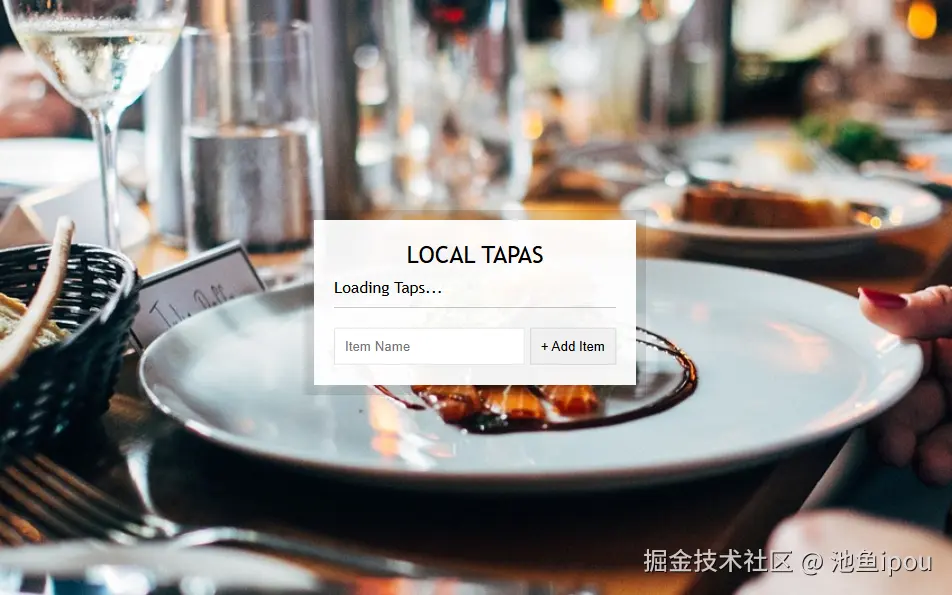

如上图所示,在重新进入界面时,之前输入的数据依然存在。这一功能的实现,正是得益于 localStorage 的使用。当用户离开页面后再回来时,他们不会丢失任何已经输入的信息,这大大提升了用户体验。而在这里我们可以通过以下步骤查看我们的localStorage在哪里,并以什么形式存储数据。

接下来我们将深入探讨这个页面的实现细节以及 localStorage 的具体用法。
代码演示
html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta data-n-head="ssr" name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, user-scalable=no, viewport-fit=cover">
<title>localStoragetitle>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html {
box-sizing: border-box;
background: url('http://wes.io/hx9M/oh-la-la.jpg') center no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
text-align: center;
font-family: Futura, "Trebuchet MS", Arial, sans-serif;
}
*,
*:before,
*:after {
box-sizing: inherit;
}
svg {
fill: white;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 50%;
width: 200px;
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
.wrapper {
padding: 20px;
max-width: 350px;
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.95);
box-shadow: 0 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
h2 {
text-align: center;
margin: 0;
font-weight: 200;
}
.plates {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
text-align: left;
list-style: none;
}
.plates li {
border-bottom: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
padding: 10px 0;
font-weight: 100;
display: flex;
}
.plates label {
flex: 1;
cursor: pointer;
}
.plates input {
display: none;
}
.plates input+label:before {
content: '⬜';
margin-right: 10px;
}
.plates input:checked+label:before {
content: '';
}
.add-items {
margin-top: 20px;
}
.add-items input {
padding: 10px;
outline: 0;

border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<h2>LOCAL TAPASh2>
<p>p>
<ul class="plates">
<li>Loading Taps...li>
ul>
<form class="add-items">
<input type="text" name="item" placeholder="Item Name" required>
<input type="submit" value="+ Add Item">
form>
<script>
const addItems = document.querySelector('.add-items'); //form
const itemsList = document.querySelector('.plates'); //ul
const items = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('items')) || [];
//event 是事件对象 1.内部this指向提交的表单 2.运行时分配event对象
function addItem(event) {
//阻止默认行为
event.preventDefault();
//.querySelector()体现了性能 优化
const text = (this.querySelector('[name=item]')).value.trim();
//创建新项对象
const item = {
text,//es6
done: false
}
items.push(item);
//更新DOM树
populateList(items, itemsList);
//存储数据 更新本地存储
localStorage.setItem('items', JSON.stringify(items));
清空输入框准备下一次输入
this.reset();
}
//渲染ul
function populateList(plates, platesList) {
platesList.innerHTML = plates.map((plate, i) => {
return `
${i}
id="item${i}"
${plate.done ? 'checked' : ''}
>
">${plate.text}
`
}).join(''); //去除页面中的“,”
}
addItems.addEventListener('submit', addItem)
populateList(items, itemsList);
//// 处理复选框状态变更
itemsList.addEventListener('change', function (event) {
if (event.target.type === 'checkbox') {
const index = event.target.dataset.index;
items[index].done = event.target.checked;
localStorage.setItem('items', JSON.stringify(items));
}
});
script>
div>
body>
html>
代码流程解析HTML 和 CSS 编写
HTML与CSS部分构建了页面的基础结构和视觉样式。这部分较为基础,主要定义了页面元素及其样式,如表单、无序列表等,并设置了全局样式规则以确保一致性和美观性,对于想要深入了解这部分内容的朋友,可以通过查阅相关代码获取更多信息。
JavaScript 实现逻辑详解初始化与加载现有数据
在JavaScript中,我们首先使用querySelector方法选择DOM中的.add-items表单和.plates无序列表元素,并创建了一个名为items的常量。该常量从浏览器的localStorage中读取名为items的数据项。如果localStorage中没有找到对应的键值对,则初始化为空数组。这一步骤确保了用户返回页面时能看到之前添加的所有项。
添加新项到列表
function addItem(event) {
......
}
当用户提交表单时,addItem函数被触发。它首先阻止了表单的默认提交行为,然后获取输入框中的文本,并将其与一个done属性(初始为false)一起包装成一个新的对象item。接着,这个新对象被添加到items数组中,调用populateList函数更新DOM,将最新的数据保存回localStorage,并重置表单以便用户继续添加更多项。
渲染列表
function populateList(plates, platesList) {
platesList.innerHTML = plates.map((plate, i) => {
......
}).join(''); // 去除页面中的逗号
}
populateList函数负责根据当前items数组的状态构建HTML列表。它遍历plates数组,为每个元素创建一个标签,包括一个复选框和标签文字。这些标签随后被合并成一个完整的字符串并赋值给platesList.innerHTML,从而实现DOM的批量更新。
用户交互:更新项状态
itemsList.addEventListener('change', function(event) {
......
});
为了保持复选框状态的一致性,我们在itemsList上监听change事件。每当复选框状态改变时,会找到对应的项并更新其done属性,最后再次保存更新后的items数组到localStorage中,以确保状态的持久化。
关键代码解释对于代码考点的思考HTML5localStorage简介
它允许开发者以键值对的形式保存数据,并且这些数据不会因为浏览器关闭或页面刷新而丢失。每个源都有大约5MB的存储空间可用。