- 作者:老汪软件技巧
- 发表时间:2024-11-25 00:03
- 浏览量:
无限连接
服务器实现协议实现
本质上,浏览器发起一个HTTP请求,服务器用HTTP状态进行响应,包括以下标头:
Content-Type: text/event-stream
Cache-Control: no-cache
Connection: keep-alive
SSE指定事件流的MIME类型必须为 text/event-stream ,浏览器不应该缓存数据,并且连接应该是持久的( keep-alive )。
消息格式
事件流是使用UTF-8编码的文本或Base64编码的二进制消息,并使用gzip压缩。每条消息由一行或多行字段组成,格式为 field-name : field-value 。每个字段以 \n 结尾。以冒号开头的行是注释,会被浏览器忽略。每个推送可以由多个消息组成,以空行分隔( \n\n )。
关键字段包括:示例:Python实现SSE
from flask import Flask, Response
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/events')
def sse_handler():
def generate():
paragraph = [
"Hello, this is an example of a continuous text output.",
"It contains multiple sentences, each of which will be sent to the client as an event.",
"This is to simulate the functionality of Server-Sent Events (SSE).",
"We can use this method to push real-time updates.",
"End of sample text, thank you!",
]
for sentence in paragraph:
yield f"data: {sentence}\n\n"
import time
time.sleep(1)
return Response(generate(), mimetype='text/event-stream')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8081, debug=True)
示例:Go实现SSE
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"time"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/events", sseHandler)
fmt.Println("Starting server on :8080")
if err := http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Server error: %v", err)
}
}
func sseHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
flusher, ok := w.(http.Flusher)
if !ok {
http.Error(w, "Streaming unsupported!", http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/event-stream")
w.Header().Set("Cache-Control", "no-cache")
w.Header().Set("Connection", "keep-alive")

// Change the output here to a specific text
paragraph := []string{
"Hello, this is an example of a continuous text output.",
"It contains multiple sentences, each of which will be sent to the client as an event.",
"This is to simulate the functionality of Server-Sent Events (SSE).",
"We can use this method to push real-time updates.",
"End of sample text, thank you!",
}
for _, sentence := range paragraph {
_, err := fmt.Fprintf(w, "data: %s\n\n", sentence)
if err != nil {
return
}
flusher.Flush()
time.Sleep(1 * time.Second) // Wait 1 second before sending the next piece of text
}
}
浏览器API️
在客户端,JavaScript的 EventSource API允许您创建一个 EventSource 对象来侦听服务器发送的事件。一旦连接上,服务器就可以向浏览器发送事件消息。浏览器通过监听 onmessage 、 onopen 和 onerror 事件来处理这些消息。
html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>SSE Example title>
head>
<body>
<h1>Server-Sent Events Example h1>
<div id="messages">div>
<script>
window.onload = function() {
if (typeof(EventSource) !== "undefined") {
const eventSource = new EventSource('/events');
eventSource.onmessage = function(event) {
const newElement = document.createElement("p");
newElement.textContent = "Message: " + event.data;
document.getElementById("messages").appendChild(newElement);
};
eventSource.onerror = function(event) {
console.error("Error occurred: ", event);
const newElement = document.createElement("p");
newElement.textContent = "An error occurred while connecting to the event source.";
document.getElementById("messages").appendChild(newElement);
eventSource.close();
};
} else {
document.getElementById("messages").textContent = "Sorry, your browser does not support server-sent events...";
}
};
script>
body>
html>
SSE调试
目前,许多流行的工具,如Postman、Insomnia、Bruno和ThunderClient缺乏对服务器发送事件SSE的足够支持。在开发过程中,这种限制会让人非常沮丧。幸运的是,我最近遇到了EchoAPI,这个工具提供了出色的SSE调试功能。这个发现极大地改善了我的工作流程,提高了效率和生产力。
如果您正在使用SSE或进行API调试,我强烈建议您尝试一下EchoAPI。它可以彻底改变您的调试体验并简化您的开发工作。更多信息请访问
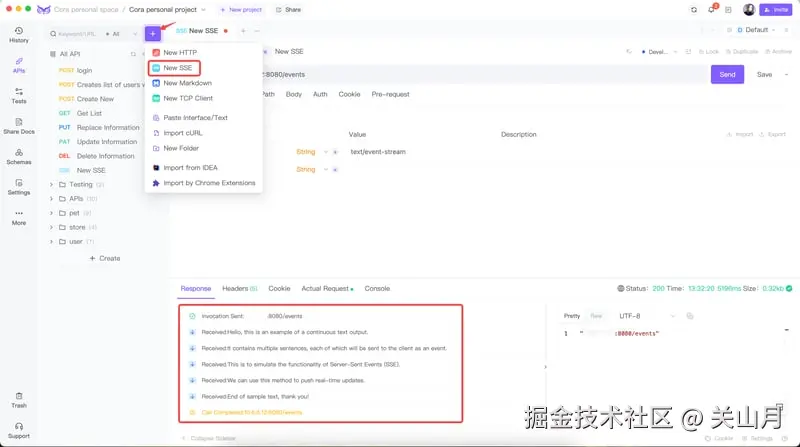
示例:SSE的EchoAPI客户端
在EchoAPI中,使用SSE接口非常简单。只需输入URL,填写相关参数,然后点击“发送”即可看到您的请求结果。