- 作者:老汪软件技巧
- 发表时间:2024-10-31 17:01
- 浏览量:162
1、题目1:226-翻转二叉树
题目:/problems/in…
类型:简单
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
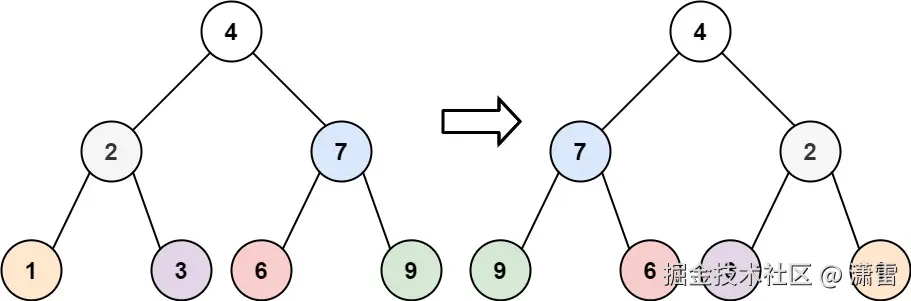
输入: root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9] 输出: [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
思路1:递归法
建议采用前序遍历或后续遍历。前左右。
递归写法:
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return root;
}
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
swapChildren(root);
return root;
}
private void swapChildren(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
}
注意:本题如果要采用中序处理的话,不太建议,如果要写,就遍历两次左边,因为子树做了交换。
思路2:层序遍历法
public TreeNode invertTree2(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return null;
}
ArrayDeque queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (queue.size()>0){
int size = queue.size();
while (size-- >0){
TreeNode pop = queue.pop();
swapChildren(pop);
if(pop.left!=null){
queue.offer(pop.left);
}
if(pop.right !=null){
queue.offer(pop.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
private void swapChildren(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
}
2、题目2:101-对称二叉树(递归)
题目:/problems/sy…
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
输入: root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 输出: true
判断左子树和右子树是否可以翻转,比较的是外侧的节点。
二叉树的题目确定顺序是非常重要的。我们这题目只能使用后序,因为我们要不断收集左右孩子的节点给上一个节点,将比较结果的信息返回上一层。
public class Number101_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(2);
node.left = new TreeNode(3);
node.right = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode(2);
node2.left = new TreeNode(4);
node2.right = new TreeNode(4);
treeNode.left = node;
treeNode.right =node2;
System.out.println(isSymmetric(treeNode));
}
public static boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return compareRes(root.left, root.right);
}
private static boolean compareRes(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
//边界条件
if(left == null && right!=null) return false;
if(left !=null && right == null) return false;
if(left == null && right == null) return true;
if(left.val != right.val) return false;
// 每一层的逻辑,比较的是镜像的数据
boolean innerRes = compareRes(left.right, right.left);
boolean outRes = compareRes(left.left, right.right);
if(innerRes && outRes){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
3、题目3:104-二叉树的最大深度(递归)
题目:/problems/ma…
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
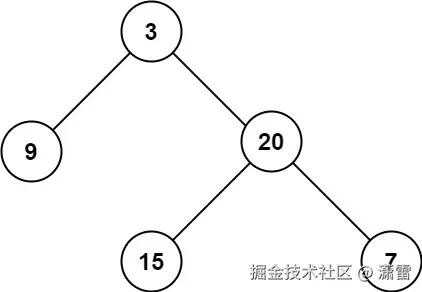
输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出: 3
思路:
先搞清楚深度和高度,
例如上面的15的高度是1,深度是3。如果求高度,是从下往上遍历,那只能用后序,如果要求深度,从上往下遍历,则采用前序。
但是因为高度和深度相等,所以给出的高度答案也是可以通过的
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);//左
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);//右
int hegiht = 1+ Math.max(leftHeight,rightHeight);//中
return hegiht;
}
}
使用层序遍历解决:用层序遍历是挺容易的。
public int maxDepth2(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int height = 0;
while (queue.size()>0){
int size =queue.size();
height++;
while (size-- >0){
TreeNode pop = queue.pop();
if(pop.left!=null){
queue.offer(pop.left);
}
if(pop.right !=null){
queue.offer(pop.right);
}
}
}
return height;
}
4、题目4:111-二叉树的最小深度
题目:/problems/mi…
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
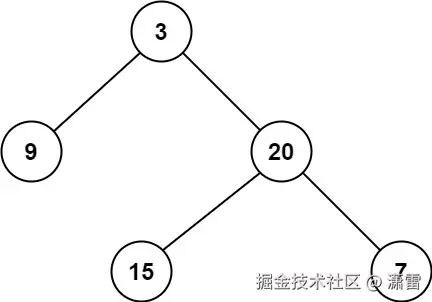
输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出: 2
思路:层序遍历我觉得很容易找到深度啥的,所以先用层序遍历试试解决。
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (queue.size()>0){
int size =queue.size();
depth++;
while (size-- >0){
TreeNode node = queue.pop();
if(node.left == null && node.right ==null){
return depth;
}
if(node.left !=null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right !=null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
再考虑迭代的思想,
public int minDepth2(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = minDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = minDepth(root.right);
if(root.left == null){
return rightDepth+1;
}
if(root.right == null){
return leftDepth+1;
}
// 左右节点都不为null
return Math.min(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1;
}