- 作者:老汪软件技巧
- 发表时间:2024-10-30 17:02
- 浏览量:
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
const startTime = performance.now();
配置请求并发送:在请求的onload、onerror等事件处理函数中记录结束时间并计算耗时:
xhr.onload = function () {
const endTime = performance.now();
const duration = endTime - startTime;
console.log(`Request took ${duration} milliseconds.`);
};
xhr.onerror = function () {
const endTime = performance.now();
const duration = endTime - startTime;
console.log(`Request took ${duration} milliseconds with error.`);
};
三、利用拦截器(axios)
如果使用axios或类似的库,可以设置请求拦截器和响应拦截器:
axios.interceptors.request.use((config) => {
config.startTime = performance.now();
return config;
});
axios.interceptors.response.use(
(response) => {
const endTime = performance.now();
const duration = endTime - response.config.startTime;
console.log(`Request to ${response.config.url} took ${duration} milliseconds.`);
return response;
},
(error) => {
const endTime = performance.now();
const duration = endTime - error.config.startTime;
console.log(`Request to ${error.config.url} took ${duration} milliseconds with error.`);
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
总结
上面都属于一些初级手段,因为还是在浏览器进程里面, 一旦出现长任务阻塞了浏览器, 这个统计就不太准确了。
进阶手段 - Performance API
Performance API:performance.getEntriesByType('resource') 可以获取请求资源类的资源加载情况, 里面就有
Performance API 提供了一系列的性能测量工具,可以测量网页加载和运行过程中的各种性能指标。其中,可以通过以下方式来统计网络请求的耗时:
使用performance.timing:
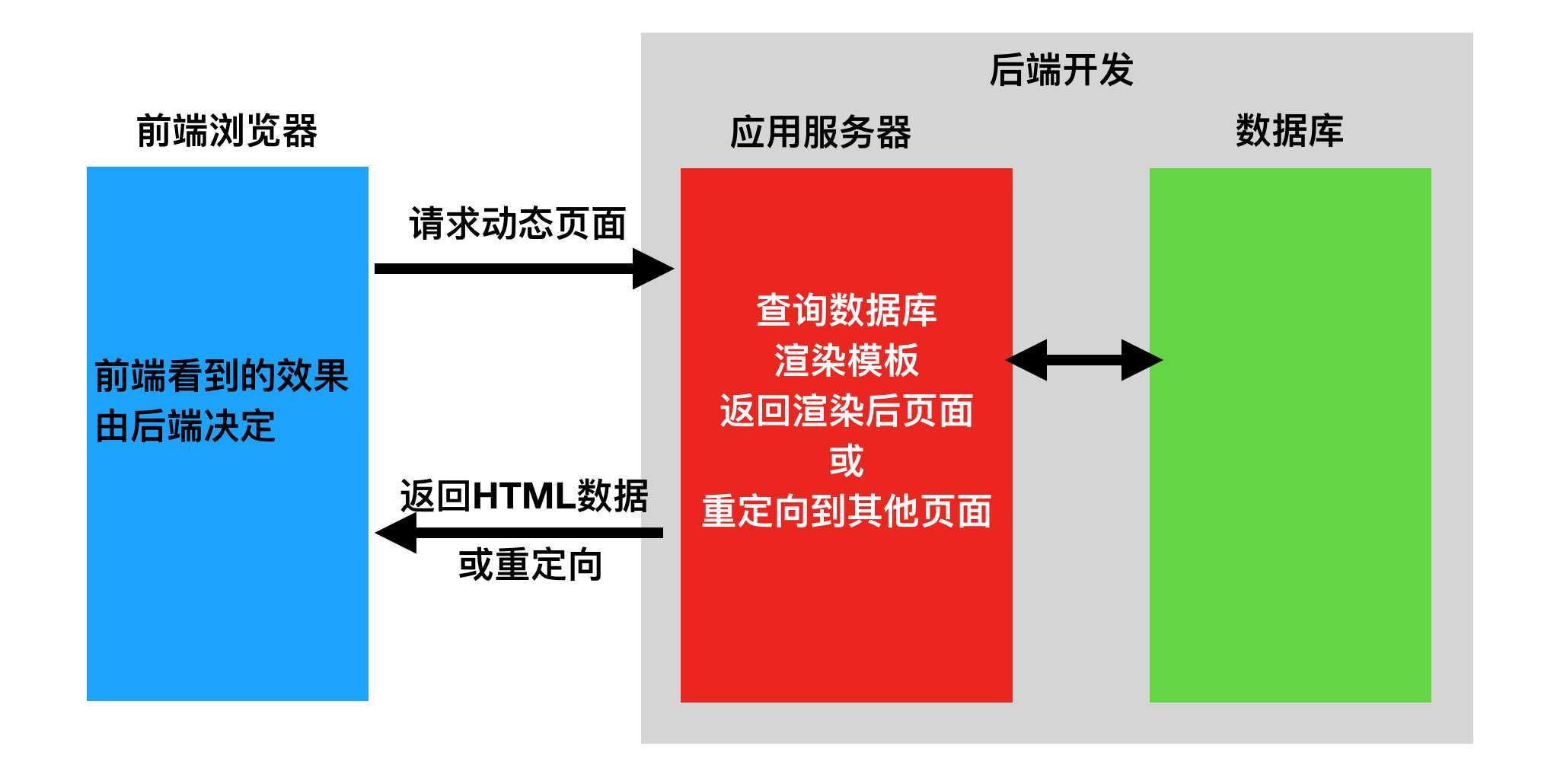
使用performance.getEntriesByType('resource'):
以下是一个示例代码:
// 遍历所有资源加载条目,找到特定请求并计算耗时
const resources = performance.getEntriesByType("resource");
for (const resource of resources) {
// 指定请求连接诶
if (resource.name === "https://example.com/specific-resource") {
console.log(`Specific resource request took ${resource.duration} milliseconds.`);
break;
}
}
高级手段 - Web Worker
Web Worker 可以用于统计请求耗时。
以下是一种使用 Web Worker 统计请求耗时的方法:
创建一个 Web Worker 文件,例如worker.js:
self.onmessage = function (event) {
const url = event.data.url;
const startTime = performance.now();
fetch(url)
.then((response) => {
const endTime = performance.now();
const duration = endTime - startTime;
self.postMessage({ duration });
})
.catch((error) => {
self.postMessage({ error: `Error fetching ${url}: ${error}` });
});
};
在主页面中使用 Web Worker:
const worker = new Worker("worker.js");
const url = "your-api-url";
worker.postMessage({ url });
worker.onmessage = function (event) {
if (event.data.duration) {
console.log(`Request to ${url} took ${event.data.duration} milliseconds.`);
} else {
console.error(event.data.error);
}
};
在这个例子中,Web Worker 负责发送请求并计算耗时,然后将结果发送回主页面。这样可以在不阻塞主页面 UI 线程的情况下进行请求耗时统计。